Build Your First Text-to-sql App
Text-to-SQL lets you ask questions in plain English and turns them into database commands, so you can work with your data without coding. In this guide, I’ll show you how to build a Text-to-SQL app that takes your questions, uses AI to translate them, runs the database query, and gives you the answer.
Build a Text-to-SQL App
We’ll do this completely free, and everything will run on your own computer. Here’s the tech stack we’ll use:
- Python: This will connect all the parts of our project.
- Ollama: This tool lets you run powerful language models like Llama 3 or Mistral on your computer.
- LangChain: This framework connects the AI to our database.
- Streamlit: This Python library turns scripts into web apps you can share in minutes.
- SQLite: A simple database that comes with Python, so you don’t need to install anything extra.
Step 1: The Setup
First, we need our AI brain. We’ll use Ollama, which lets you run models like Llama 3 or Mistral on your own computer.
Start by downloading Ollama by visiting ollama.com and installing it.
Next, pull a model. Open your terminal or command prompt and type:
ollama pull llama3
Then, make a new folder for your project, open your terminal in that folder, and run:
pip install langchain langchain-community langchain-ollama streamlit
Step 2: Creating the Database
We need some data to work with. We’ll write a simple Python script to make a sample SQLite database with student grades.
Create a file called create_db.py and run it once:
import sqlite3
# Connect to SQLite database (or create it if it doesn't exist)
connection = sqlite3.connect("student_grades.db")
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Create a table
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS grades (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
subject TEXT,
score INTEGER,
grade TEXT
)
""")
# Insert some dummy data
data = [
(1, "Aman", "Math", 95, "A"),
(2, "Anshu", "Math", 78, "C"),
(3, "Akshu", "History", 88, "B"),
(4, "Rahul", "History", 92, "A"),
(5, "Divyansh", "Science", 85, "B"),
(6, "Nandini", "Math", 65, "D")
]
cursor.executemany("INSERT OR IGNORE INTO grades VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)", data)
connection.commit()
connection.close()
print("Database created and populated successfully!")Run this script in your terminal. You’ll see a file called student_grades.db show up in your folder.
Step 3: The Logic
Now we’ll use LangChain to connect our local Llama 3 model to the database.
Create a file called app.py. Start by importing the tools you need:
import streamlit as st
from langchain_community.utilities import SQLDatabase
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# Page Setup
st.set_page_config(page_title="Text-to-SQL App", layout="centered")
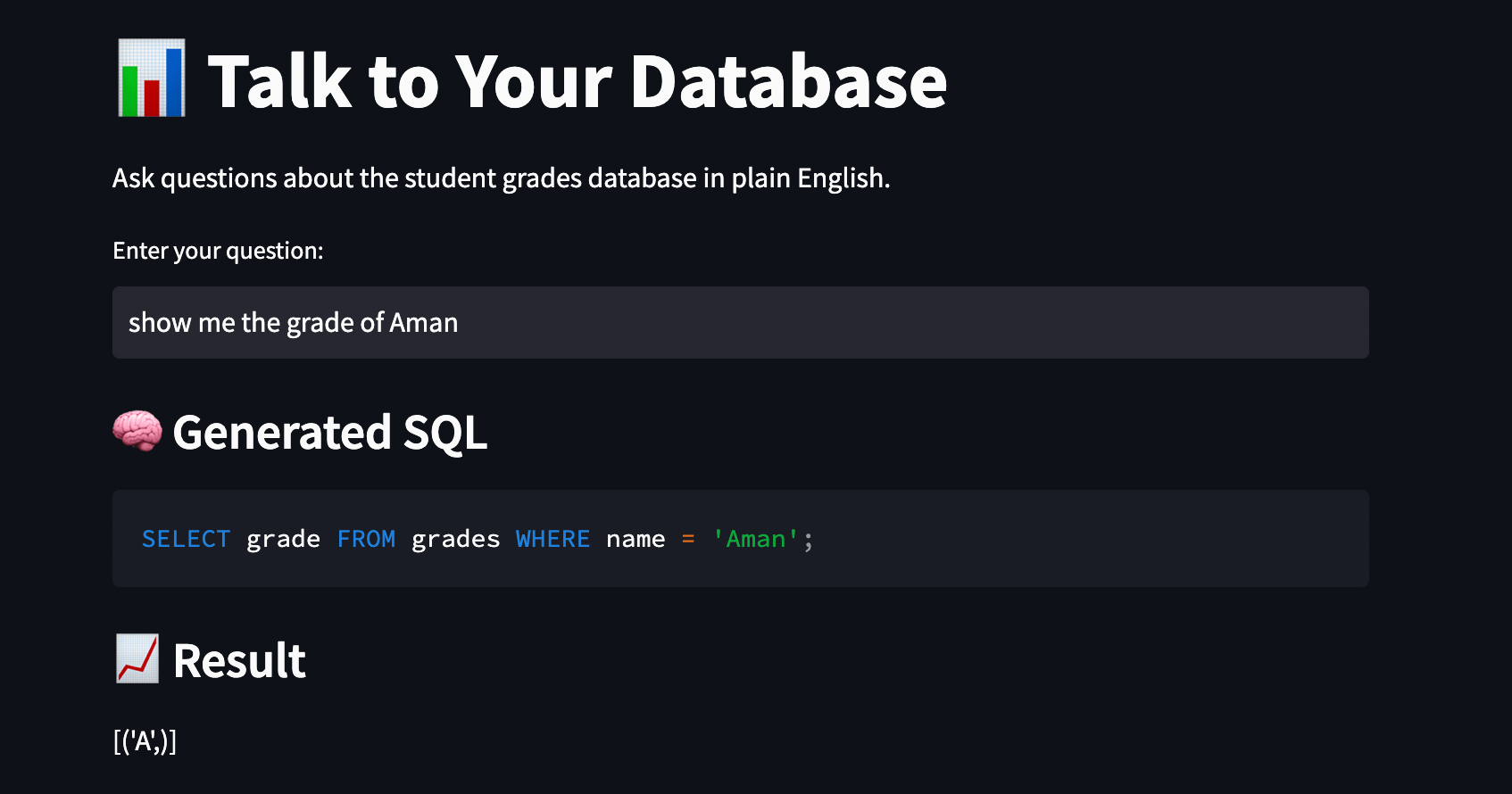
st.title("???? Talk to Your Database")
st.write("Ask questions about the student grades database in plain English.")
# Database Connection
db = SQLDatabase.from_uri("sqlite:///student_grades.db")
# Local LLM (Ollama)
llm = ChatOllama(
model="llama3",
temperature=0
)
# Prompt (LCEL Style)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("""
You are a senior data analyst and SQL expert.
Given the database schema below, write a correct SQL query
that answers the user's question.
Rules:
- Use only the tables and columns in the schema
- Do NOT explain anything
- Return ONLY the SQL query
Schema:
{schema}
Question:
{question}
""")
# LCEL Runnable Pipeline
sql_chain = (
prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
schema = db.get_table_info()Here, SQLDatabase.from_uri gives the database file to LangChain. Setting temperature=0 keeps the AI from being creative with SQL syntax, so it stays precise.
Step 4: The User Interface
Now finish app.py by adding the input box and the code to run your queries. Add this to your file:
# UI Input
question = st.text_input(
"Enter your question:",
placeholder="e.g., Who scored the highest in Math?"
)
# Execution
if question:
try:
sql_query = sql_chain.invoke(
{"schema": schema, "question": question}
).strip()
st.subheader("???? Generated SQL")
st.code(sql_query, language="sql")
st.subheader("???? Result")
result = db.run(sql_query)
st.write(result)
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"❌ Error: {e}")
# Footer
st.markdown("---")
st.caption("Powered by LangChain 1.x • Ollama • Llama 3 • Streamlit")Next, open your terminal and start the Streamlit app:
streamlit run app.py
A browser window will open and show your interface. Try asking:
- “Show me all grades for Aman.”
- “What is the average score in Math?”
- “Who got a D?”
You’ll see the AI write the SQL, run it, and show you the result!
Closing Thoughts
That’s how you build a Text-to-SQL app.
I used to spend about 30% of my time writing simple SQL queries for business managers. When you build tools like this, especially with bigger, secure databases like Postgres or Snowflake, you help non-technical teams get answers on their own, right away.
If you found this article helpful, you can follow me on Instagram for daily AI tips and practical resources. You may also be interested in my latest book, Hands-On GenAI, LLMs & AI Agents, a step-by-step guide to prepare you for careers in today’s AI industry.
The post Build Your First Text-to-SQL App appeared first on AmanXai by Aman Kharwal.
Popular Products
-
 Enamel Heart Pendant Necklace
Enamel Heart Pendant Necklace$49.56$24.78 -
 Digital Electronic Smart Door Lock wi...
Digital Electronic Smart Door Lock wi...$211.78$105.89 -
 Automotive CRP123X OBD2 Scanner Tool
Automotive CRP123X OBD2 Scanner Tool$649.56$324.78 -
 Portable USB Rechargeable Hand Warmer...
Portable USB Rechargeable Hand Warmer...$61.56$30.78 -
 Portable Car Jump Starter Booster - 2...
Portable Car Jump Starter Booster - 2...$425.56$212.78